Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
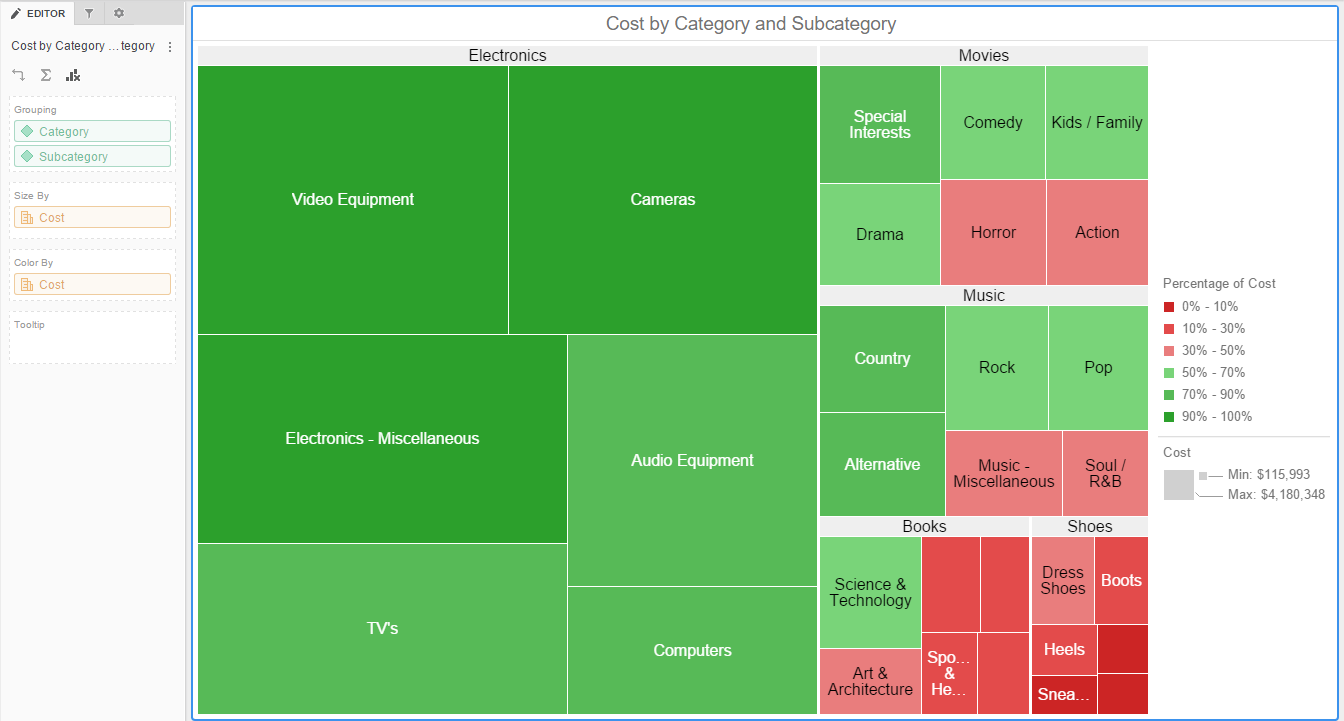
Heat maps are powerful visualization tools transforming raw data into easily digestible, color-coded representations. They effectively communicate complex information at a glance, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden within spreadsheets or databases. This visual approach significantly enhances understanding and facilitates informed decision-making across diverse fields. The underlying principle involves mapping data values onto a two-dimensional grid, with color intensity representing the magnitude of each data point. Warmer colors (reds, oranges) typically indicate higher values, while cooler colors (blues, greens) represent lower values. This simple yet effective methodology allows for quick identification of hotspots, outliers, and overall data distribution.
Applications Across Industries:
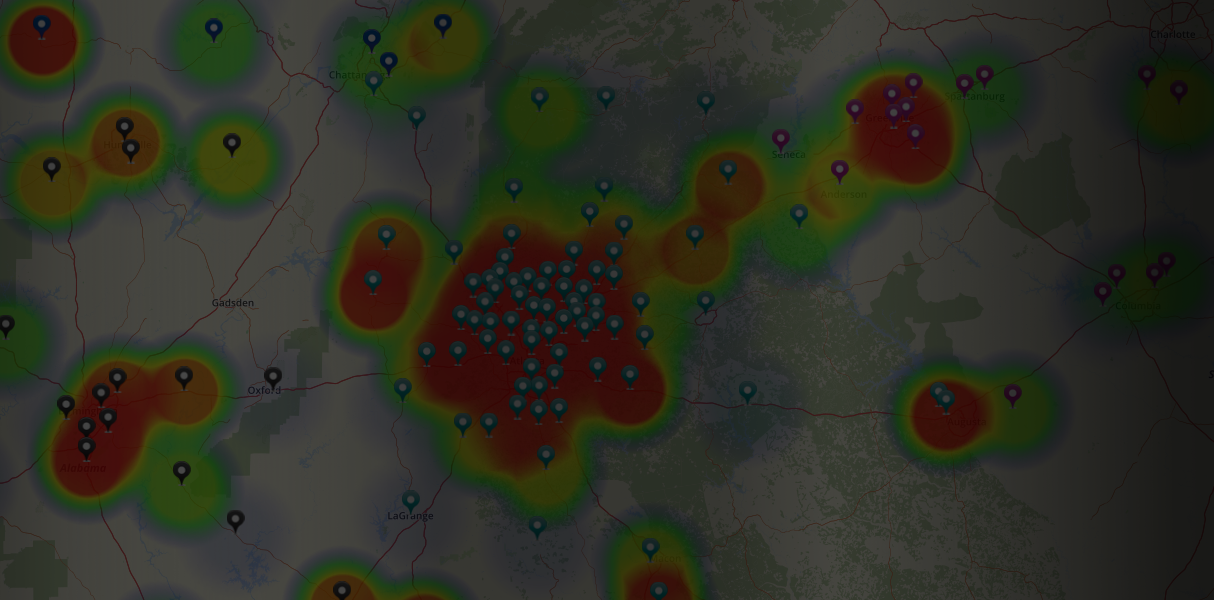
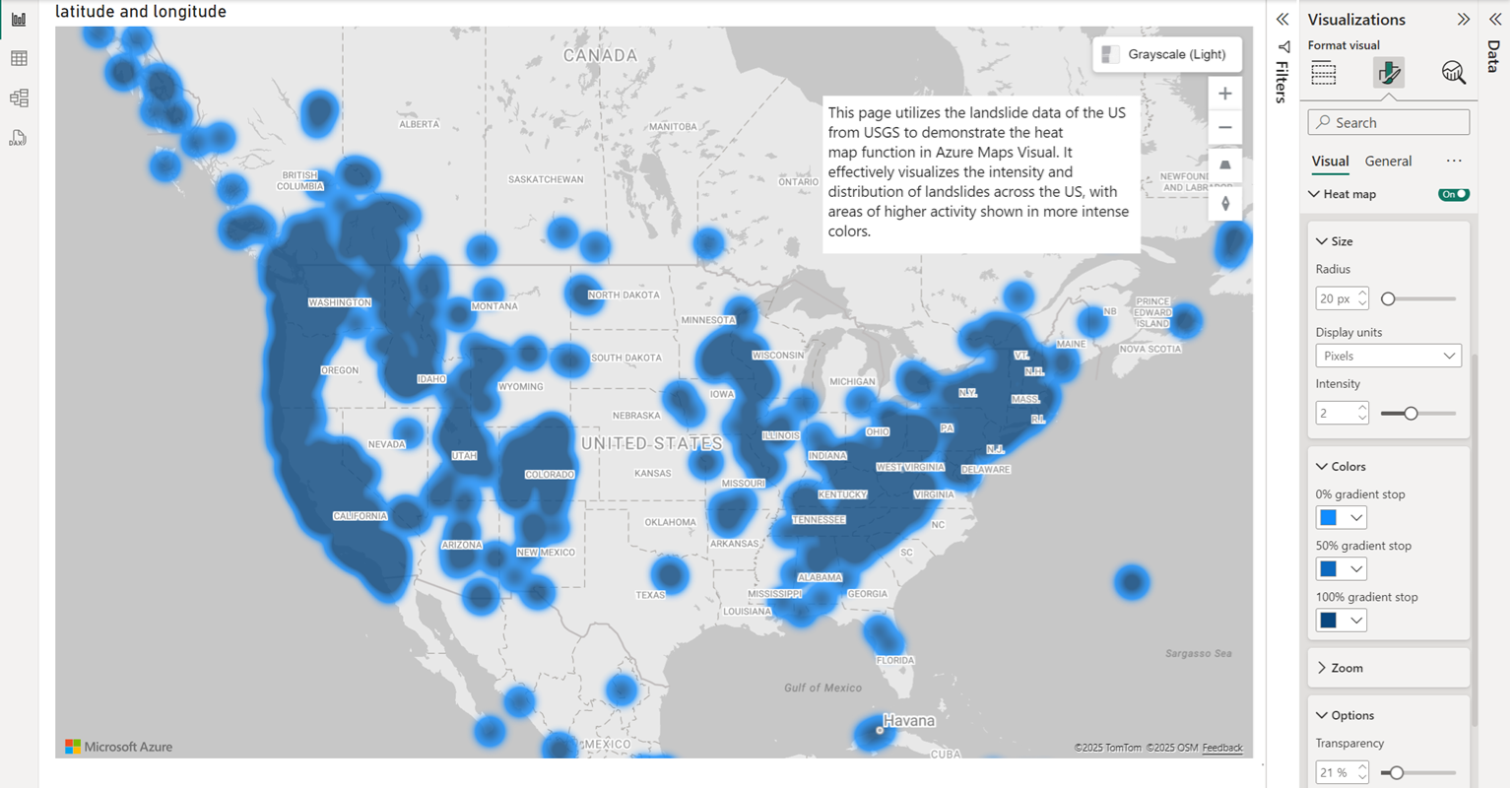
The versatility of these visual aids extends across numerous sectors. In website analytics, they pinpoint areas of user engagement or frustration on web pages. Marketing departments leverage them to understand customer behavior, optimize campaign effectiveness, and identify high-performing product offerings. In manufacturing, these tools can reveal production bottlenecks or areas needing improvement in efficiency. Geographic information systems (GIS) utilize them to display spatial data, illustrating population density, crime rates, or disease outbreaks. Even in the realm of finance, they can be used to analyze market trends, risk assessment, or portfolio performance. The applications are virtually limitless, limited only by the creativity in data application.
Types and Functionality:
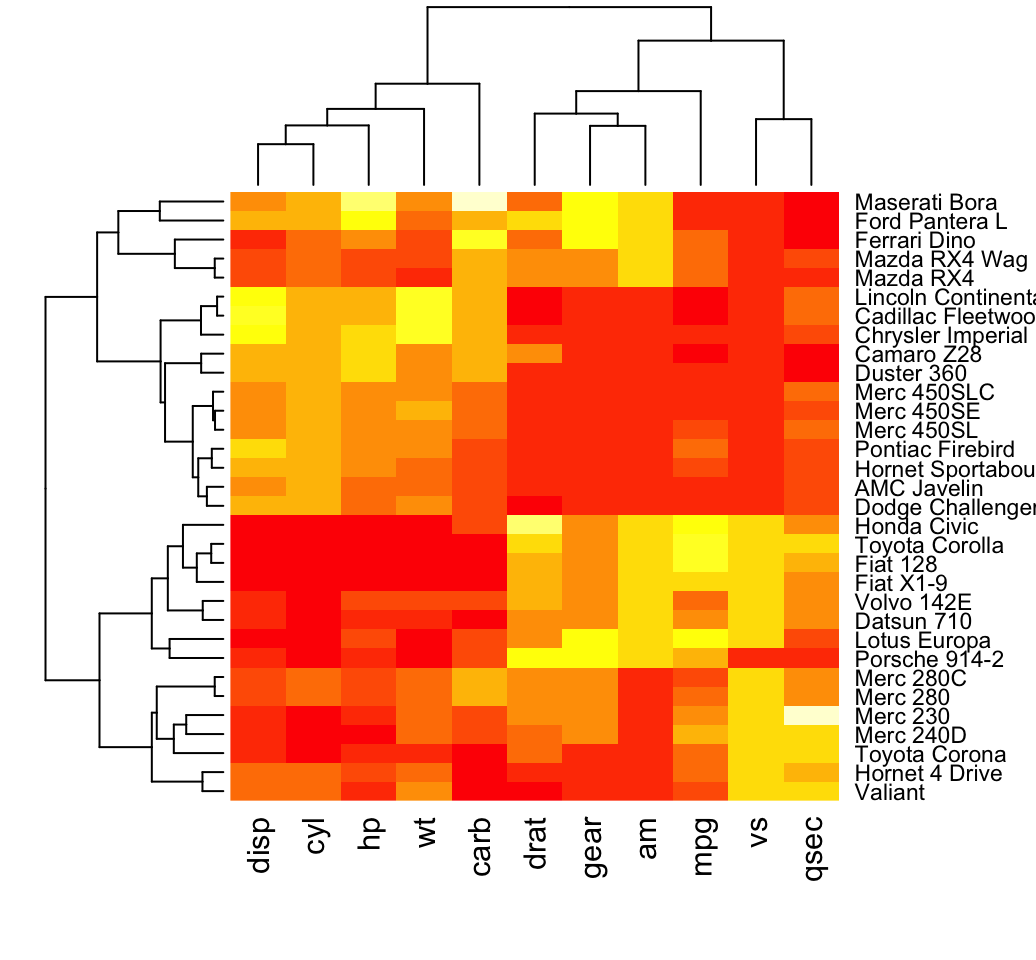
Several types of these visual representations cater to specific analytical needs. Standard heat maps display data across a single variable, using color gradients to represent its magnitude. Clustered heat maps group similar data points together, enhancing pattern recognition. Sequential heat maps utilize a single color scale, progressing from light to dark, making them ideal for showing continuous data. Diverging heat maps use a color scale that diverges from a central neutral point, effectively highlighting both positive and negative deviations. Each type offers unique advantages, allowing for tailored visualization based on the specific data and analytical goals. The choice depends heavily on the nature of the data and the insights sought.
Data Preparation and Interpretation:
Effective utilization begins with meticulous data preparation. Data must be accurately collected, cleaned, and organized to ensure meaningful interpretation. Missing values need to be addressed, outliers identified, and data appropriately scaled to avoid misrepresentation. Careful consideration should be given to the chosen color scheme, ensuring clarity and avoiding perceptual biases. The legend should clearly define the color-value relationship, enabling accurate data interpretation. Understanding the limitations of the visualization is crucial; they primarily showcase trends and patterns, not causal relationships. Further investigation might be needed to confirm observed patterns.
Benefits and Advantages:
The advantages of this visual approach are numerous. They dramatically improve data understanding by presenting complex information in a concise and easily digestible format. This leads to quicker identification of key trends and patterns, facilitating faster decision-making. They facilitate effective communication of findings to diverse audiences, regardless of their technical expertise. The visual nature enhances engagement and memorability, making data insights more impactful. Furthermore, they promote collaborative data exploration, fostering better teamwork and knowledge sharing. Finally, they aid in identifying areas requiring further investigation, guiding subsequent data analysis and refining strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What types of data are suitable for heat map visualization?
- A: Numerical data, both continuous and discrete, is best suited. Categorical data can be incorporated but requires careful consideration of representation.
-
Q: What software is available for creating heat maps?
- A: Numerous software packages, including specialized statistical software, spreadsheet programs (like Excel and Google Sheets), data visualization tools (Tableau, Power BI), and programming languages (R, Python), offer heat map generation capabilities.
-
Q: How can accuracy be ensured when interpreting a heat map?
- A: Careful attention to data preparation, appropriate color scales, clear legends, and an understanding of the visualization’s limitations are crucial for accurate interpretation. Always consider potential biases and contextual factors.
-
Q: Can heat maps be used for predictive modeling?
- A: While heat maps themselves do not perform predictive modeling, they can reveal patterns and trends that inform predictive models. They can be a valuable tool in exploratory data analysis preceding model development.
Tips for Effective Heat Map Creation:
- Choose the appropriate heat map type: Select the type that best suits the data and analytical goals.
- Use a clear and consistent color scheme: Avoid overly complex or distracting color palettes.
- Provide a clear and informative legend: Ensure the color-value relationship is easily understood.
- Label axes and data points appropriately: Enhance clarity and facilitate interpretation.
- Consider the audience: Tailor the visualization to the audience’s understanding and needs.
- Maintain data integrity: Ensure data accuracy and address missing values appropriately.
Conclusion:
Visual data analysis tools such as heat maps represent a significant advancement in data interpretation and communication. Their ability to transform complex datasets into readily understandable visual representations significantly enhances decision-making processes across various domains. By providing a clear, concise, and engaging way to understand data patterns, they facilitate more informed strategies, improved efficiency, and a deeper understanding of underlying trends. The continued development and refinement of these tools promise even greater potential for extracting valuable insights from increasingly complex datasets. Their use should be considered a crucial element of any comprehensive data analysis strategy.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!