Visualizing Geographic Data: Utilizing Zip Code Radius Maps
Related Articles: Visualizing Geographic Data: Utilizing Zip Code Radius Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Geographic Data: Utilizing Zip Code Radius Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Geographic Data: Utilizing Zip Code Radius Maps
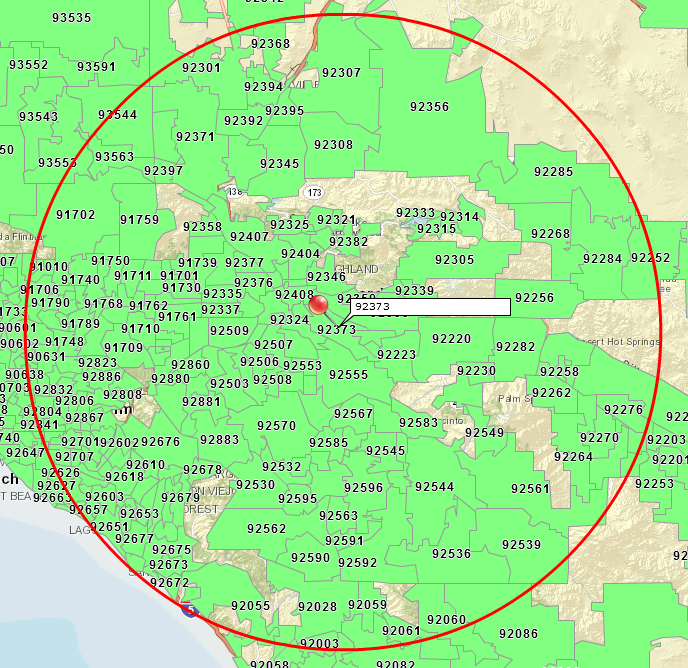
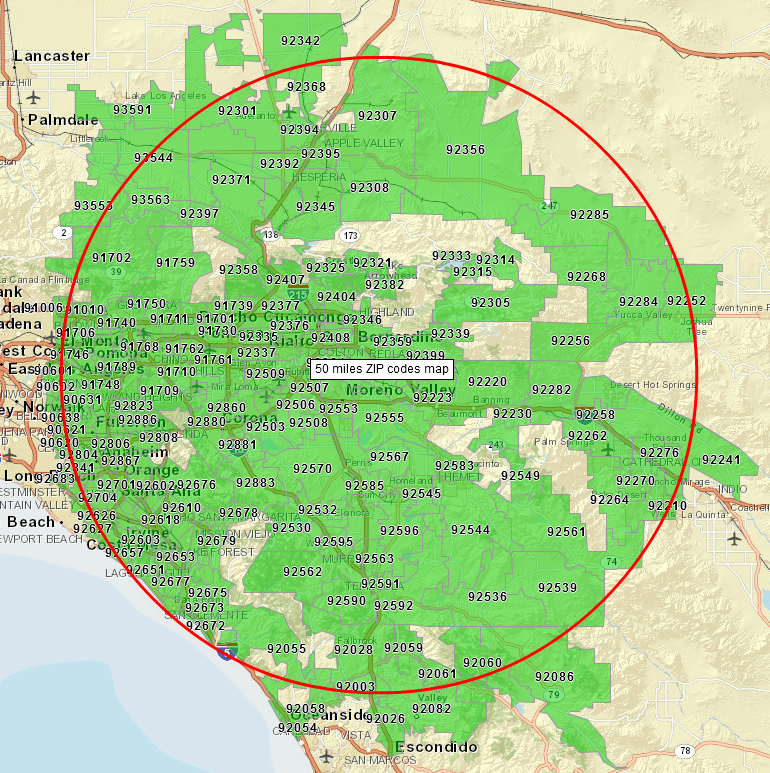
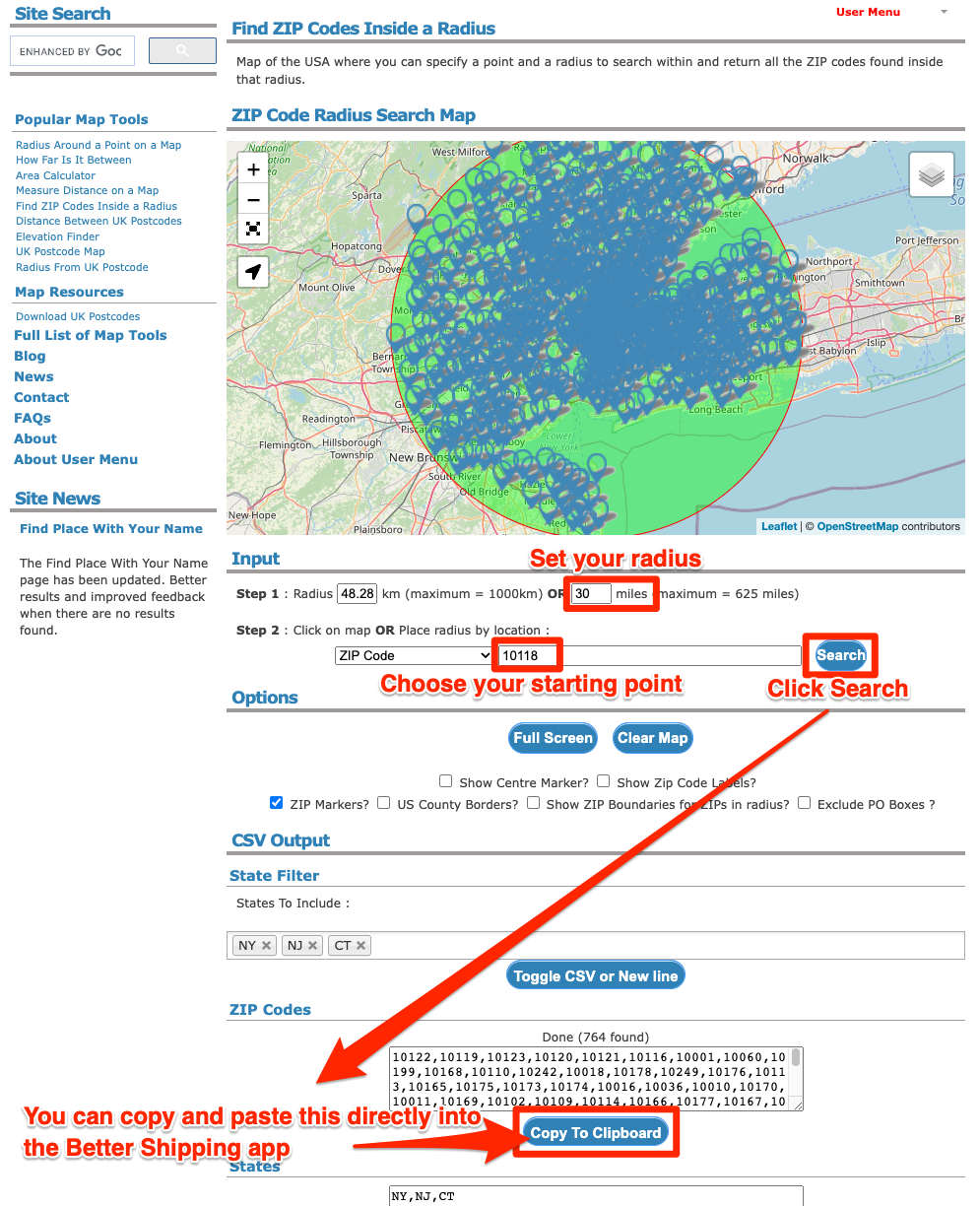
Geographic information systems (GIS) and mapping technologies have revolutionized how spatial data is analyzed and presented. One particularly useful application involves visualizing data associated with zip codes, often represented as a circular area extending a specified distance from a zip code’s centroid. This visualization offers significant advantages across various sectors, enabling more effective decision-making and strategic planning.
The creation of these maps typically begins with obtaining accurate geographic coordinates for the centroid of each zip code. This information is readily available from various data providers, often integrated into GIS software packages. Once the coordinates are secured, the process involves using mapping software to generate a circular buffer around each centroid. The radius of this buffer defines the area of interest, commonly expressed in miles or kilometers. The choice of radius depends entirely on the specific application; a smaller radius might be suitable for hyperlocal analysis, while a larger radius might be necessary for regional studies.
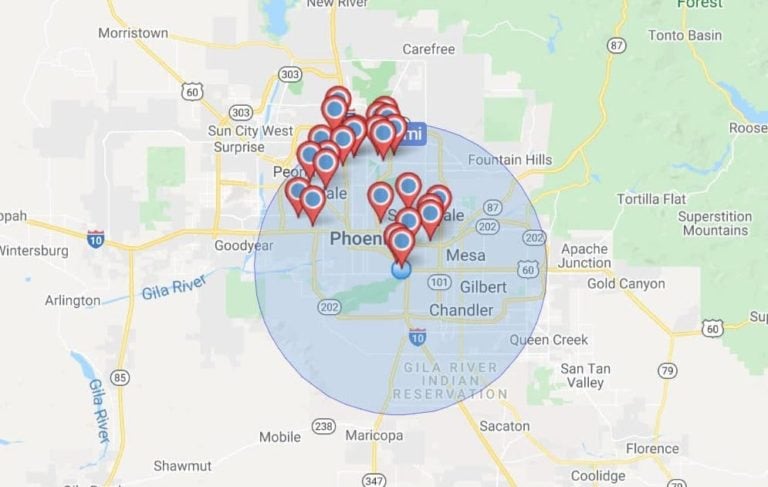
The resulting map displays the zip code areas overlaid with their respective radius buffers. This visual representation is highly beneficial for numerous applications. For instance, in market research, these maps allow businesses to identify potential customer bases within a specific geographic range of their operations. A company launching a new product might use this technique to target marketing campaigns effectively, focusing resources on areas within a chosen distance of their distribution centers or retail locations. Similarly, real estate professionals can leverage this functionality to showcase properties within a particular radius of desirable amenities, schools, or employment centers.
Beyond commercial applications, these maps are invaluable in various other fields. Emergency services can use them to delineate response areas, ensuring that resources are deployed efficiently during critical incidents. Public health officials can utilize this approach to track disease outbreaks, identify high-risk areas, and implement targeted interventions. Urban planners can incorporate this data into their models for infrastructure development, optimizing the location of new facilities based on proximity to existing services and population density within a defined radius. Furthermore, environmental agencies can use this visualization method to analyze pollution patterns, identify environmental hotspots, and develop strategies for mitigation and remediation.
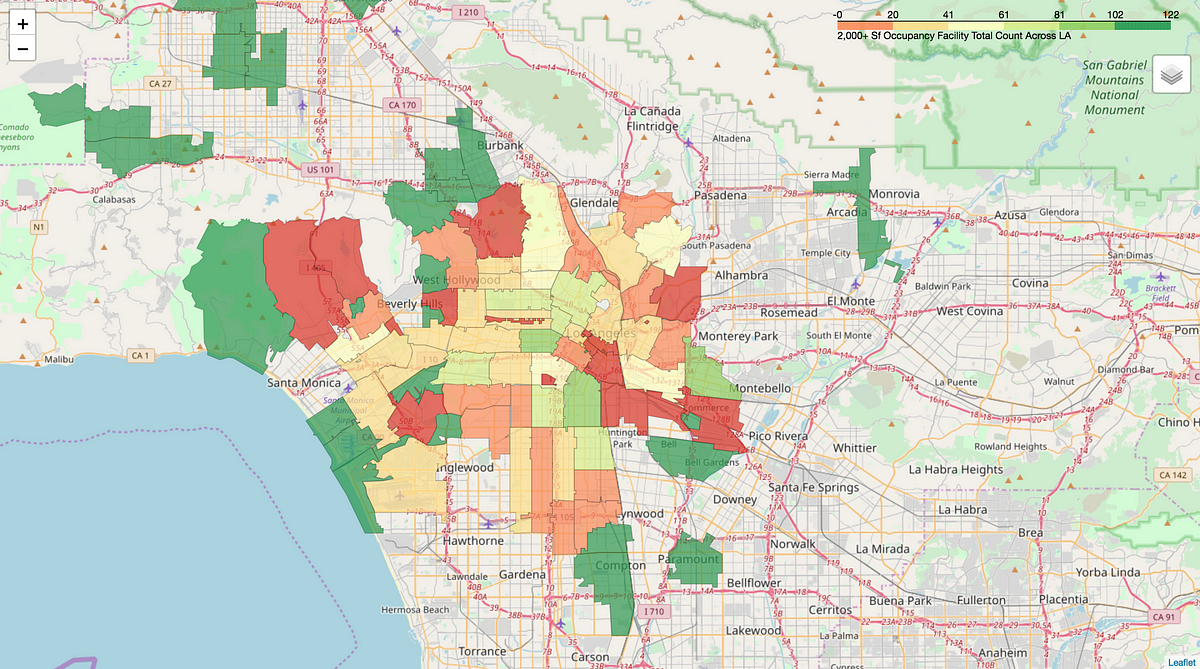
The versatility of this mapping technique extends to analyzing demographic data. By overlaying demographic information onto the zip code radius maps, researchers can gain valuable insights into population characteristics within specific geographic zones. This information can be crucial for targeted social programs, resource allocation, and public policy development. For example, understanding the distribution of age groups or income levels within a certain radius of a proposed new school can inform decisions regarding its capacity and resource requirements.
The accuracy of these maps depends heavily on the accuracy of the underlying data. The precision of zip code centroids and the chosen radius are critical factors. In addition, variations in the shape of zip code boundaries can affect the accuracy of the radius representation, particularly in areas with irregular or complex geographic features. Therefore, it is essential to utilize high-quality data sources and appropriate mapping software to ensure the reliability and validity of the generated maps.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What data is required to create a zip code radius map?
A: The primary data requirement is a database containing zip codes and their corresponding geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude). Additional data layers, such as demographic information or points of interest, can be overlaid for more comprehensive analysis.
-
Q: What software is typically used to create these maps?
A: Various GIS software packages, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo Pro, are commonly used. Many online mapping platforms also offer functionality to create these maps, albeit with potentially limited customization options.
-
Q: How is the radius determined?
A: The radius is determined based on the specific application and analytical needs. Factors to consider include the nature of the analysis, the scale of the study area, and the desired level of granularity.
-
Q: What are the limitations of these maps?
A: The accuracy of the maps is limited by the accuracy of the underlying data and the simplification inherent in representing irregular zip code boundaries as circles. Furthermore, the use of a circular buffer assumes uniform distribution within the radius, which might not always reflect reality.
Tips for Effective Utilization:
-
Data Validation: Always validate the accuracy and completeness of the underlying data before generating the map.
-
Radius Selection: Carefully consider the appropriate radius based on the specific analytical goals. Experimentation with different radii can provide valuable insights.
-
Data Overlay: Combine the radius maps with other data layers (e.g., demographic data, points of interest) to enhance the analysis.
-
Visualization Techniques: Employ clear and effective visualization techniques to communicate the information effectively. Consider using color-coding, legends, and clear labeling.
-
Software Selection: Choose mapping software that meets the specific requirements of the analysis, considering factors such as functionality, ease of use, and data handling capabilities.
Conclusion:
The ability to visualize zip code data using radius maps provides a powerful tool for spatial analysis across a wide range of disciplines. By leveraging accurate data and appropriate mapping techniques, researchers and practitioners can gain valuable insights into geographic patterns, facilitating better decision-making and strategic planning. The versatility and applicability of this mapping technique underline its importance in addressing diverse challenges and opportunities within a spatial context. Continued advancements in GIS technology and data availability will further enhance the capabilities and applications of this valuable tool.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Geographic Data: Utilizing Zip Code Radius Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!